Which Of The Following Is An E Ample Of A Lipid
Which Of The Following Is An E Ample Of A Lipid - College students require optimal brain function, which is supported by fatty fish and walnuts. Which of the following enzymes is found bound to hdl and ldl in blood plasma and acts to convert free cholesterol into cholesteryl esters? Web this vitamin e radical can be converted back to its original form by a hydrogen donor. What are functions of fats in living organisms? Vitamin c is one such donor. Vitamin e also can affect enzyme activity. What are the four major types of lipids? Fats are made up of fatty acids and either glycerol or sphingosine. There is great structural variety among the lipids, as will be demonstrated in the following sections. Fats are made up of fatty acids and either glycerol or sphingosine.
A) wax b) triacylglyceride c) eicosanoid d) steroid e) sphingolipid, which of the following is not a lipid?, which of the following is not a. In this course, you will learn about the different types of lipids, such as fats, phospholipids, and steroids, and how they are synthesized and metabolized in living organisms. Lipids are a major class of biochemical compounds that includes oils as well as fats. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like lipids are. Earwax, liquid fats called oils contain. Web lipids and fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty.
Web lipids are one of the important biological macromolecules that have diverse functions and structures. Web this vitamin e radical can be converted back to its original form by a hydrogen donor. In this course, you will learn about the different types of lipids, such as fats, phospholipids, and steroids, and how they are synthesized and metabolized in living organisms. There is great structural variety among the lipids, as will be demonstrated in the following sections. Web in this section, you will explore the following questions:
College students require optimal brain function, which is supported by fatty fish and walnuts. Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic compounds that include molecules like fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Web membrane lipids may be classified as phospholipids, glycolipids, and/or sphingolipids. In this course, you will learn about the different types of lipids, such as fats, phospholipids, and steroids, and how they are synthesized and metabolized in living organisms. Fats are a stored form of energy and are also known as triacylglycerols or triglycerides. Most of the fats found in food are triglycerides, cholesterol, and phospholipids.
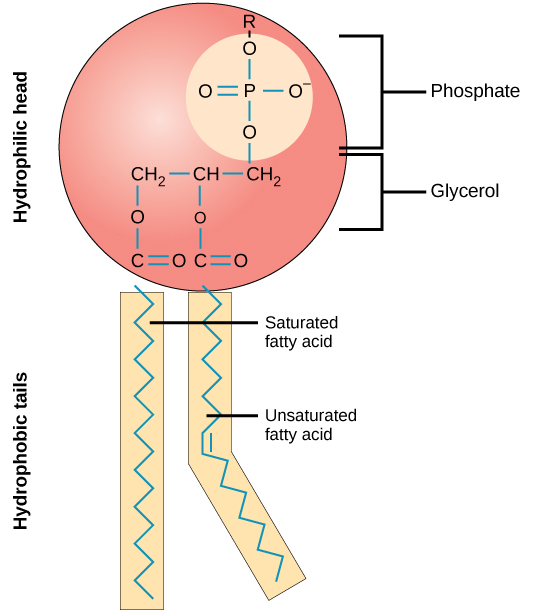
Fats are a stored form of energy and are also known as triacylglycerols or triglycerides. Openstax is part of rice university, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Integral proteins span the lipid bilayer, while peripheral proteins are more loosely associated with the surface of the membrane. The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility in nonpolar organic solvents (e.g., ether, chloroform, acetone and benzene) and general insolubility in water. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility in nonpolar organic solvents (e.g., ether, chloroform, acetone and benzene) and general insolubility in water. Proteins are another important component of biological membranes. What is the molecular structure of phospholipids, and what is the role of phospholipids in cells? Give today and help us reach more students.
There Is Great Structural Variety Among The Lipids, As Will Be Demonstrated In The Following Sections.
Lipids are a major class of biochemical compounds that includes oils as well as fats. Ether, chloroform, acetone & benzene) and general insolubility in water. The oxidation of fats and oils supplies about 9 kcal of energy for every gram oxidized, whereas the oxidation of carbohydrates supplies only 4 kcal/g. Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic compounds that include molecules like fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
You Will Also Explore The Roles Of Lipids In Membrane Structure, Energy.
Web the lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility in nonpolar organic solvents (e.g. A) wax b) triacylglyceride c) eicosanoid d) steroid e) sphingolipid, which of the following is not a lipid?, which of the following is not a. Web this vitamin e radical can be converted back to its original form by a hydrogen donor. College students require optimal brain function, which is supported by fatty fish and walnuts.
Most Of The Fats Found In Food Are Triglycerides, Cholesterol, And Phospholipids.
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a lipid is any substance of biochemical origin that is, which if the following is not a biochemical function classification for lipids?, which of the following statements concerning fatty acids is correct? The following year, bangham, his colleague malcolm standish, and gerald weissmann, an american physician, established the integrity of this closed, bilayer structure and its ability to. Gram for gram, they pack more than twice the caloric content of carbohydrates: What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
Learn More About The Structure, Types, And Functions Of Lipids In This Article.
Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. Fats are made up of fatty acids and either glycerol or sphingosine. Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. In this course, you will learn about the different types of lipids, such as fats, phospholipids, and steroids, and how they are synthesized and metabolized in living organisms.