What Do Atoms Form When They Share Electron Pairs
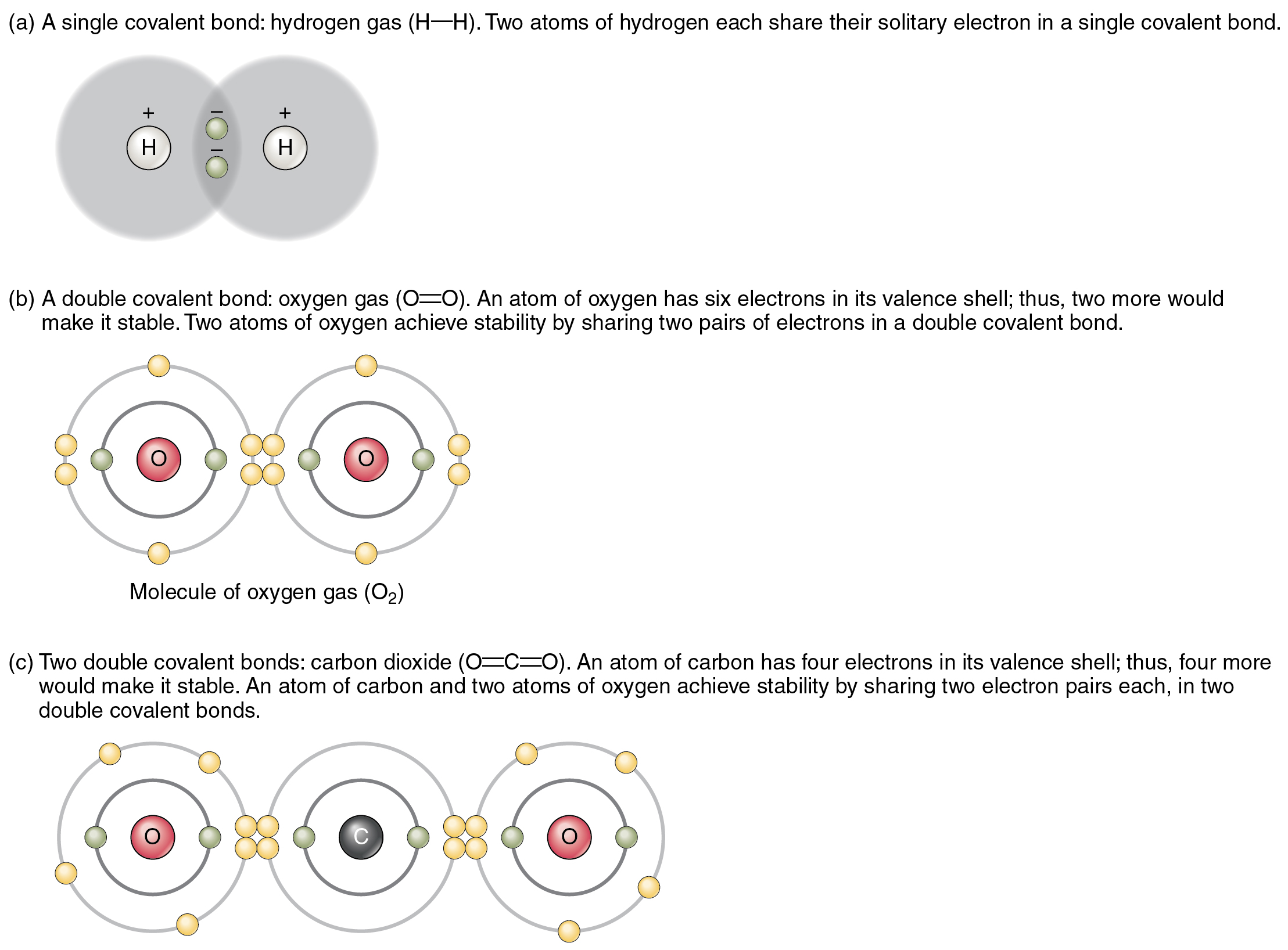
What Do Atoms Form When They Share Electron Pairs - Lewis electron dot diagrams can be drawn to illustrate covalent bond formation. Because the spins are paired, the magnetic moment of the electrons cancel one another, and the pair's contribution to magnetic properties is generally diamagnetic. Web a single shared pair of electrons is called a single bond. In a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms. This page introduces the way atoms can bond together by sharing electrons in single covalent bonds, and the various ways you can show covalent bonds on paper. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. Web covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. This is illustrated on the right. A covalent bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms.
In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms. Double bonds or triple bonds between atoms may be necessary to properly illustrate the bonding in some molecules. Web the premise of the vsepr theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. When two atoms form a covalent bond, they share their valence electrons in order to achieve an octet (8 valence electrons), except for hydrogen which bonds to achieve a duet (2 valence electrons). Lewis electron dot diagrams can be drawn to illustrate covalent bond formation. What is the difference between covalent and ionic bonding?
Web if a pair of atoms has a slight positive charge, sharing electrons lets them balance their charge and a bond is formed. A double bond forms when two atoms share two electron pairs or six electrons. In a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. This is illustrated on the right. If the atoms are identical, like two hydrogens forming \ce {h_ {2 (g)}} hx 2(g), then the bond is purely covalent.
Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. Web a double covalent bond is a covalent bond formed by atoms that share two pairs of electrons. Web a single shared pair of electrons is called a single bond. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. The two atoms are thus held together by the need to share the electron pair. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms.
Lewis electron dot diagrams can be drawn to illustrate covalent bond formation. If the atoms are identical, like two hydrogens forming \ce {h_ {2 (g)}} hx 2(g), then the bond is purely covalent. The double covalent bond that occurs between the two carbon atoms in ethane can also be represented by a structural formula and with a molecular model as shown in the figure below. Covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms.
Web the premise of the vsepr theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. Web they can form a chemical bond between two atoms, or they can occur as a lone pair of valence electrons. What is the difference between covalent and ionic bonding? This page introduces the way atoms can bond together by sharing electrons in single covalent bonds, and the various ways you can show covalent bonds on paper.
It Is This Sharing Of Electrons That We Refer To As A Chemical Bond, Or More Specifically, As A Covalent Bond, So Named Because The Bond Acts To Satisfy The Valence Of Both Atoms.
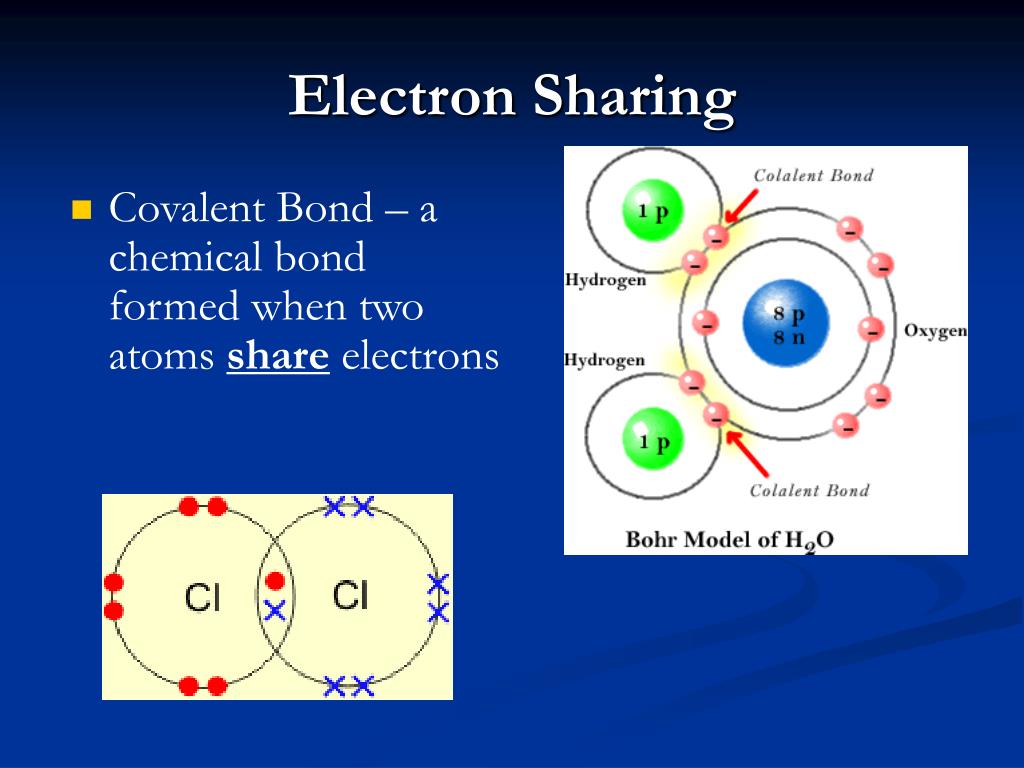
Let’s consider both types of bonds in detail. Web as we saw with the h 2 molecule in chapter 2, a bond between two atoms is formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between the atoms. In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms. Each cl atom interacts with eight valence electrons:
A Covalent Bond Forms When The Bonded Atoms Have A Lower Total Energy Than That Of Widely Separated Atoms.
The six in the lone pairs and the two in the single bond. Because the spins are paired, the magnetic moment of the electrons cancel one another, and the pair's contribution to magnetic properties is generally diamagnetic. In a single covalent bond, two atoms share one pair of electrons. Double bonds or triple bonds between atoms may be necessary to properly illustrate the bonding in some molecules.
Because Most Filled Electron Shells Have Eight Electrons In Them, Chemists Called This Tendency The Octet Rule.
An atom that shares one or more of its electrons will complete its outer shell. If the atoms are identical, like two hydrogens forming \ce {h_ {2 (g)}} hx 2(g), then the bond is purely covalent. Web a double covalent bond is a covalent bond formed by atoms that share two pairs of electrons. More than a century ago, in 1916, gilbert lewis identified the chemical bond with a pair of shared electrons in an epochal publication titled the atom and the molecule 1.
Web Covalent Bonds Are Formed When Atoms Share Electrons.
Web covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. Web the premise of the vsepr theory is that electron pairs located in bonds and lone pairs repel each other and will therefore adopt the geometry that places electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible. The two atoms are thus held together by the need to share the electron pair. This is illustrated on the right.
![[ANSWERED] What do atoms form when they equally share electron](https://i2.wp.com/media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question-candidate/20220511034952883386-4536923.jpg?h=512)