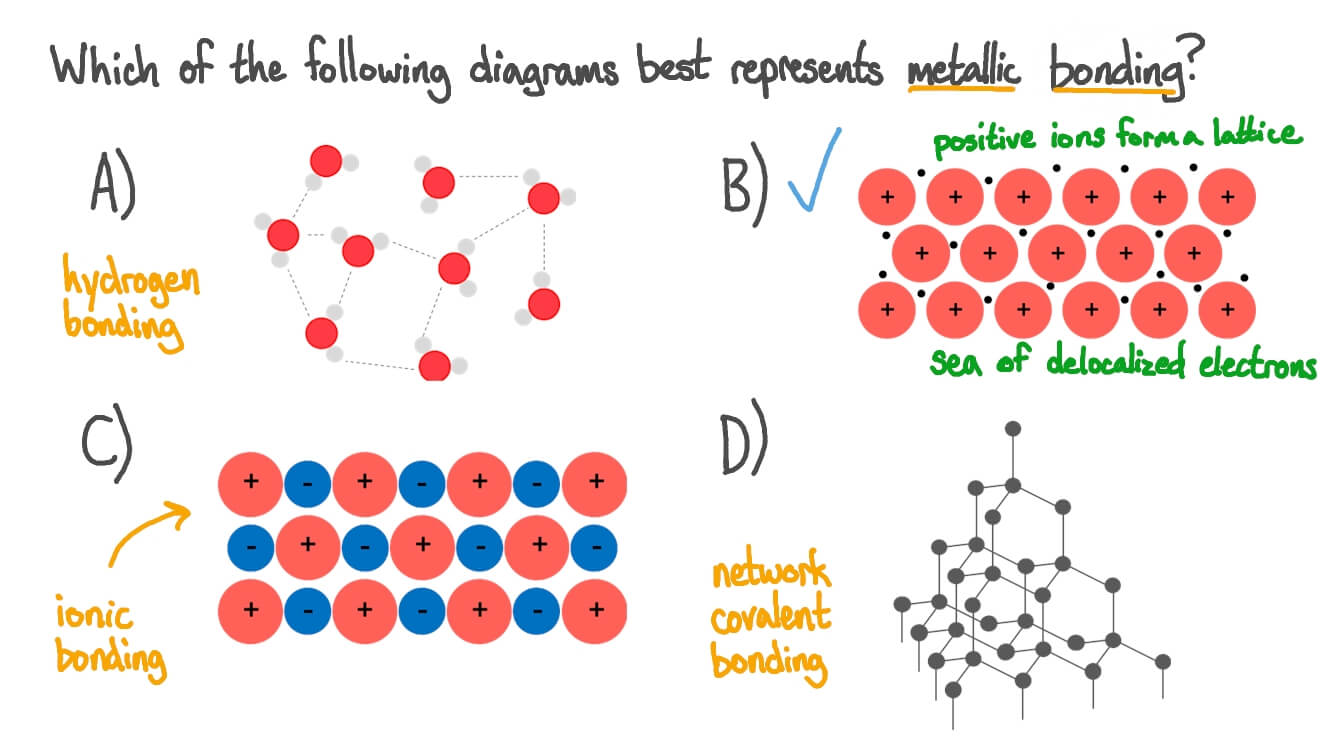
Metallic Bonding Drawing
Metallic Bonding Drawing - The arrangement of the atoms in a metal. Even a metal like sodium (melting point 97.8°c) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the periodic table. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which a ‘cloud’ of free moving valence electrons is bonded to the positively charged ions in a metal. The structure and bonding in a substance are. Metals are said to be giant structures since they usually contain lots of atoms. Delocalised electrons are free to. Web it's like ionic bonding but with a sea of electrons. Metallic bonding is a type of strong chemical bond that occurs in pure metals and alloys. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Everything you need to teach metallic bonding.
Metallic bonds are strong, so metals can maintain a regular structure. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. The extra electrons on the outer shell leave the atom, making the metal a positive ion. Describe, at the simplest level, the origin of electron bands in metals. Metallic bonding is the strong. Is the attraction between the positive ions in a regular lattice and the. 269 views 1 year ago united states.
1.4.9 properties of metallic substances; It is uniquely challenging and coherent, crafted by subject experts to ensure that all pupils achieve broad, deep subject expertise. Solidify your students’ understanding of the structure and properties of metals and alloys. How to draw wembley fraggle from. An example of this is a copper wire or an aluminum sheet.
In metallic bonding, metals become cations and release out electrons in the open. 1.4.9 properties of metallic substances; Metallic bonds are strong, so metals can maintain a regular structure. Delocalised electrons are free to. Metallic bonding is a type of strong chemical bond that occurs in pure metals and alloys. Is the attraction between the positive ions in a regular lattice and the.
It is uniquely challenging and coherent, crafted by subject experts to ensure that all pupils achieve broad, deep subject expertise. Describe how the electrical and thermal conductivity of metals can be explained according to band theory. Metals tend to form cations. An example of this is a copper wire or an aluminum sheet. Even a metal like sodium (melting point 97.8°c) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the periodic table.
Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which a ‘cloud’ of free moving valence electrons is bonded to the positively charged ions in a metal. Metallic bonding is a type of strong chemical bond that occurs in pure metals and alloys. The properties of a metal can. The arrangement of the atoms in a metal.
1.4.8 Properties Of Covalent Substances;
Web it's like ionic bonding but with a sea of electrons. Metallic bonding is the strong. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond in which a ‘cloud’ of free moving valence electrons is bonded to the positively charged ions in a metal. Metallic bonding in transition elements.
1.4.5 Dot & Cross Diagrams;
Web know how metals bond with one another. The extra electrons on the outer shell leave the atom, making the metal a positive ion. When there are many of these cations, there are also lots of electrons. The structure of metallic bonds is entirely different from that of ionic and covalent bonds.
The Properties Of A Metal Can.
Web metallic bonds are strong and are a result of the attraction between the positive metal ions and the negatively charged delocalised electrons. Describe how the electrical and thermal conductivity of metals can be explained according to band theory. Metallic bonding forms between metals and metals. Metallic bonds are strong, so metals can maintain a regular structure.
We Prioritise The Core Academic Subjects That Are Strong Preparation For Further Study, Understanding Of The World And Fulfilling Lives.
Delocalised electrons are free to. The top region is where bonds are mostly ionic, the lower left region is where bonding is metallic, and the lower right region is where the bonding is covalent. Web vdom dhtml tml>. Of attraction between the metal ions and the delocalised electrons.