Dimorphic Fungus E Ample
Dimorphic Fungus E Ample - Dimorphic fungi are organisms that have the ability to switch between two morphologies during their lifecycle: Web in this review, we focus on the phenomenon of fungal dimorphism among plant pathogens, and we present a brief summary of the current knowledge about dimorphic plant pathogenic fungi. Web dimorphic switching requires the fungus to sense and respond to the host environment and is essential for pathogenicity. This morphologic switch, known as the phase transition, defines the biology and lifestyle of these fungi. Symptoms of active infection include. Diseases caused by dimorphic phytopathogenic and systemic dimorphic fungi have markedly increased in prevalence in the last decades, and understanding the morphogenic transition to the virulent state might yield novel means of controlling dimorphic fungi. Dimorphic fungi can live in four different forms; When tested in vitro against coccidioides mycelia, rifampicin, isoniazid, and ethambutol had very high mics (8500 μg/ml, 500 μg/ml, and 2500 μg/ml, respectively 72 ). Here we focus on a group of evolutionarily related fungal pathogens of humans known as the thermally dimorphic fungi. The ability of pathogenic fungi to switch between a multicellular hyphal and unicellular yeast growth form is a tightly regulated process known as dimorphic switching.
Mold, hyphal, filamentous or as a yeast. Mnemonics to remember dimorphic fungi. Web dimorphic switching requires the fungus to sense and respond to the host environment and is essential for pathogenicity. We begin by discussing the extensively studied model plant pathogen u. When tested in vitro against coccidioides mycelia, rifampicin, isoniazid, and ethambutol had very high mics (8500 μg/ml, 500 μg/ml, and 2500 μg/ml, respectively 72 ). Web we have described a highly conserved hybrid histidine kinase, drk1, that is indispensable for dimorphism, virulence gene expression, and pathogenicity in dimorphic fungi. Symptoms of active infection include.
Symptoms of active infection include. Web dimorphic switching requires the fungus to sense and respond to the host environment and is essential for pathogenicity. Many species of dimorphic fungi are pathogenic to humans and other organisms. When tested in vitro against coccidioides mycelia, rifampicin, isoniazid, and ethambutol had very high mics (8500 μg/ml, 500 μg/ml, and 2500 μg/ml, respectively 72 ). Web dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold [1] and yeast.
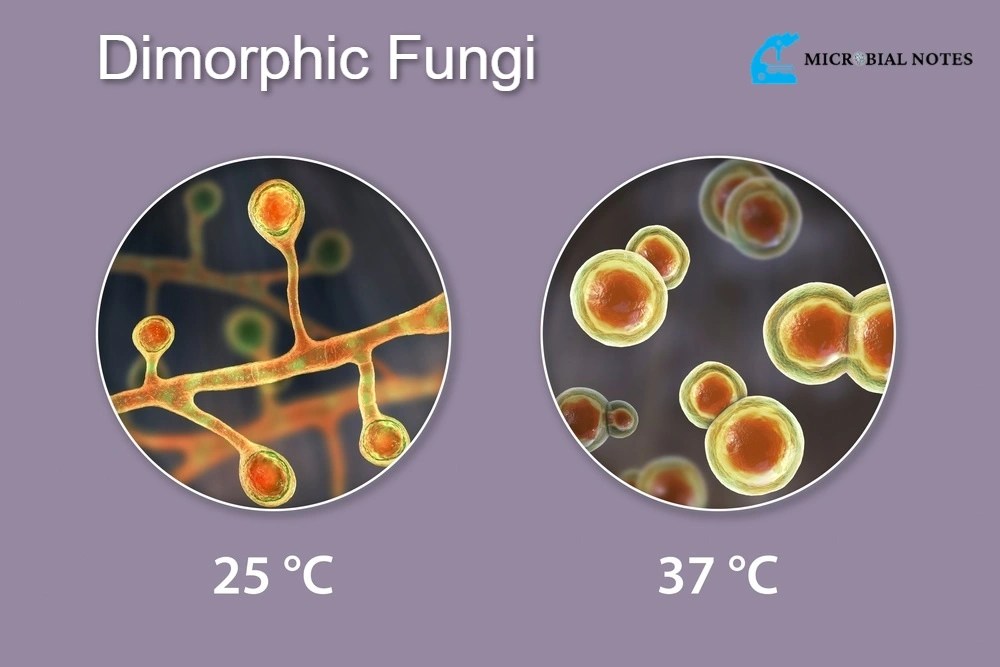
This is usually brought about by change in temperature and the fungi are also described as thermally dimorphic fungi. Dimorphic fungi can live in four different forms; We begin by discussing the extensively studied model plant pathogen u. Dimorphic fungi are significant pathogens and can cause severe infections in humans and animals. The ability of pathogenic fungi to switch between a multicellular hyphal and unicellular yeast growth form is a tightly regulated process known as dimorphic switching. Symptoms of active infection include.
Web dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold [1] and yeast. Symptoms of active infection include. This is usually brought about by change in temperature and the fungi are also described as thermally dimorphic fungi. Here we focus on a group of evolutionarily related fungal pathogens of humans known as the thermally dimorphic fungi. These dimorphic fungi have adapted to switch between multicellular filamentous growth or hyphae to unicellular growth forms or yeasts.
Dimorphic fungi are significant pathogens and can cause severe infections in humans and animals. Dimorphic fungi are organisms that have the ability to switch between two morphologies during their lifecycle: Mold, hyphal, filamentous or as a yeast. Many species of dimorphic fungi are pathogenic to humans and other organisms.
Web In This Review, We Focus On The Phenomenon Of Fungal Dimorphism Among Plant Pathogens, And We Present A Brief Summary Of The Current Knowledge About Dimorphic Plant Pathogenic Fungi.
The ability of pathogenic fungi to switch between a multicellular hyphal and unicellular yeast growth form is a tightly regulated process known as dimorphic switching. Web we have described a highly conserved hybrid histidine kinase, drk1, that is indispensable for dimorphism, virulence gene expression, and pathogenicity in dimorphic fungi. We begin by discussing the extensively studied model plant pathogen u. This morphologic switch, known as the phase transition, defines the biology and lifestyle of these fungi.
Colony Morphology Of Dimorphic Fungi.
Web dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold [1] and yeast. Importance of dimorphic fungi in human health and disease. Symptoms of active infection include. This review will focus on the role of dimorphism in fungi commonly called thermally dimorphic fungi, which switch to a yeast growth form during infection.
These Dimorphic Fungi Have Adapted To Switch Between Multicellular Filamentous Growth Or Hyphae To Unicellular Growth Forms Or Yeasts.
Many species of dimorphic fungi are pathogenic to humans and other organisms. Mnemonics to remember dimorphic fungi. Disease caused by dimorphic fungi. Web these pathogens are thermally dimorphic fungi.
Dimorphic Fungi Can Live In Four Different Forms;
Mold, hyphal, filamentous or as a yeast. [2] an example is talaromyces marneffei, [3] a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature. Dimorphic fungi are found in three main phyla, namely: Dimorphic fungi are significant pathogens and can cause severe infections in humans and animals.