2 1 Additional Practice Slope Intercept Form
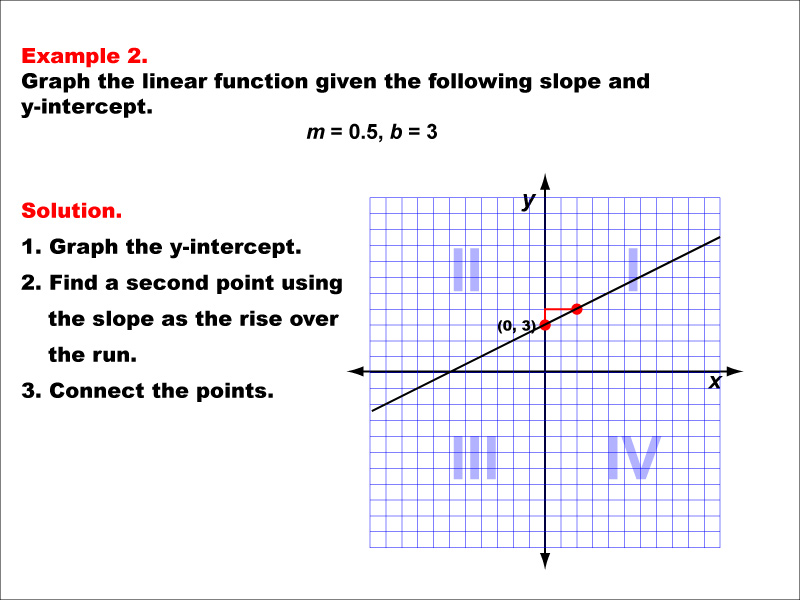
2 1 Additional Practice Slope Intercept Form - It has the following general structure. Y = −5x + 1. Put all these values together to construct the slope intercept form of a linear equation: Y+ 3 = −2 (x+ 1) 3. − 2 = 2(x + 3) 2. Y = 10 − 100 x. −4 −2 −2 o −4 2 y 2 x 4. Video tutorial on slope intercept form. Y = −5x + 1 2. Y + 3 = −2(x + 1) 3.
Y = mx + b. Y = −5x + 1 2. Y = −5x + 1. −4 −2 −2 o −4 2 y 2 x 4. (−1, 3) and (−3, 1) 6. Web math resources algebra graphing linear equations. Y = mx + b.
Y = __ 2 x. −4 −2 o 2 4 −2. Web envision™ algebra 1 • teaching resources. Graph the line that represents each linear equation. − 2 = 2(x + 3) 2.
(−4, 8) and (4, 6) 7. Y = −5x + 1. Y = 3 2 x − 5. Let's graph y = 2 x + 3. Graph the line that represents each linear equation. Web envision™ algebra 1 • teaching resources.
Let's graph y = 2 x + 3. Graph the line that represents each linear equation. Y = −5x + 1. Y+ 3 = −2 (x+ 1) 3. (−1, 3) and (−3, 1) 6.
−4 −2 −2 o −4 2 y 2 x 4. Y = x + 3. Y = __ 2 x. You can also use x₂ and y₂ instead of x₁ and y₁ here.
Here, M And B Can Be Any Two Real Numbers.
Let's graph y = 2 x + 3. This article is here to help! In general, the slope intercept form assumes the formula: Y = −5x + 1.
Y = −5X + 1 2.
Y = x + 3. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Graph the line that represents each linear equation. Y = mx + b.
−4 −2 O 2 4 −2.
Graph the line that represents each linear equation. Y = mx + b. Y = − 3 x + 2.7. Y = m x + b.
( − 2, 0) ( 0, − 2) D.
Y = mx + b. You can also use x₂ and y₂ instead of x₁ and y₁ here. But this equation has x in the last term! Graphing lines with integer slopes.